Securing Critical Infrastructure: The Role of Line-Interactive UPS
UPS (uninterruptible power supply) systems are essential for protecting critical infrastructure in healthcare and finance. They provide backup power in the event of a power outage, ensuring that sensitive equipment and data are protected. Line-interactive UPS systems are a popular choice for these applications, offering a number of advantages over other types of UPS systems.
Visit Our UPS Systems Study Course
Benefits of Line-Interactive UPS Systems
Line-interactive UPS systems offer a number of benefits over other types of UPS systems, including:
Lower cost: Line-interactive UPS systems are typically less expensive than other types of UPS systems, making them a more cost-effective option for businesses on a budget.
Smaller size: Line-interactive UPS systems are also smaller than other types of UPS systems, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
Lower maintenance: Line-interactive UPS systems require less maintenance than other types of UPS systems, making them a more hassle-free option for businesses.
Types of Line-Interactive UPS Systems
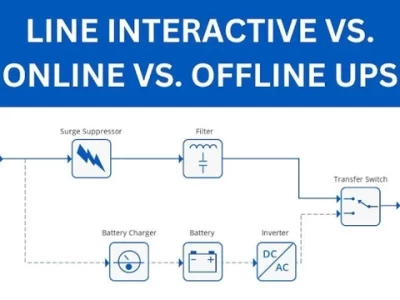
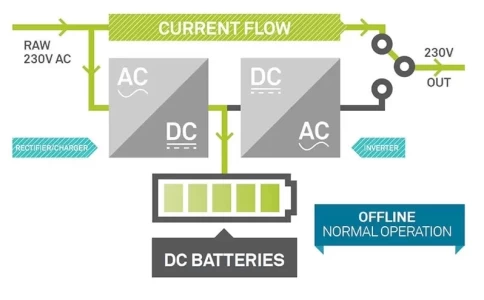
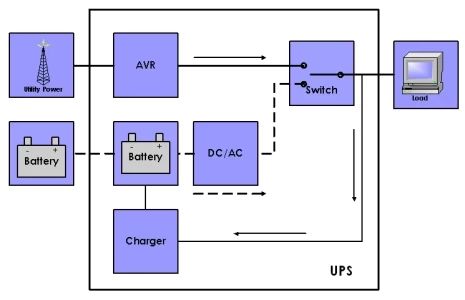
There are two main types of line-interactive UPS systems: standby and online. Standby UPS systems only provide power when the primary power source fails, while online UPS systems provide continuous power, even during power outages.
Standby UPS systems are typically less expensive than online UPS systems, but they also offer less protection. They are a good choice for applications where the risk of a power outage is low.
Online UPS systems are more expensive than standby UPS systems, but they offer more protection. They are a good choice for applications where the risk of a power outage is high, such as hospitals and data centers.
Performance of Line-Interactive UPS Systems
The performance of a line-interactive UPS system is determined by a number of factors, including:
Power output: The power output of a UPS system is measured in VA (volt-amps). It must be sufficient to power the equipment it is protecting.
Runtime: The runtime of a UPS system is the amount of time that it can provide power during a power outage. The runtime of a UPS system is determined by the size of its battery.
Efficiency: The efficiency of a UPS system measures how much power it loses during conversion. A more efficient UPS system will lose less power and be more cost-effective to operate.
Technical Considerations
There are a number of technical considerations that must be taken into account when selecting a line-interactive UPS system, including:
Input voltage: The input voltage of a UPS system is the voltage of the power source that it is connected to. The input voltage of a UPS system must be compatible with the voltage of the power source.
Output voltage: A UPS system's output voltage is the power it supplies to its connected equipment. It must be compatible with the voltage of the equipment it is protecting.
Frequency: The frequency of a UPS system is the rate at which it converts power. The frequency of a UPS system must be compatible with the frequency of the power source.
Across the healthcare and financial sectors, where the consequences of downtime range from inconvenient to life-threatening or financially devastating, line-interactive UPS systems play a silent but vital role. Their ability to provide clean power, instant backup, and facilitate safe shutdown procedures acts as an indispensable insurance policy for critical infrastructure. As power grids evolve and technologies advance, the integration of UPS protection will remain deeply intertwined with maintaining resilience and reliable service delivery in these vital sectors.