Assessing the Limitations of Line-Interactive UPS
Assessing the Limitations of Line-Interactive UPS
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) are a crucial safeguard for ensuring the continuous operation of critical systems. Line-interactive UPS systems, a popular choice for small and medium-sized environments, offer a balance of affordability and protection. However, these systems face limitations when subjected to high power demands or frequent power fluctuations, potentially affecting their performance and reliability.
Visit Our UPS Systems Study Course
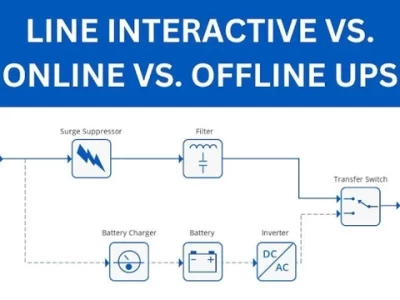
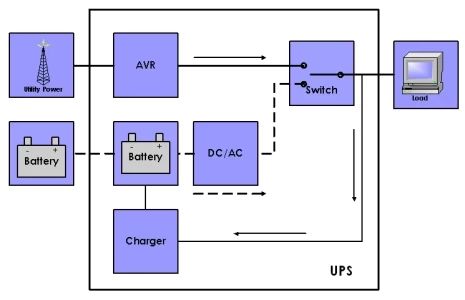
Understanding Line-Interactive UPS Systems
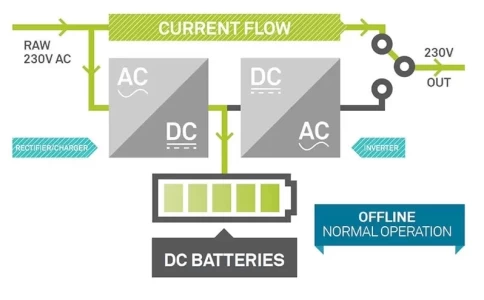
Line-interactive UPS systems derive their name from their interactive relationship with the input power line. They feature a voltage regulation transformer that can boost or reduce voltage to compensate for under and over-voltages. During normal operation, line-interactive units draw power to both supply connected equipment and charge the backup battery. In the event of a power failure, an inverter quickly switches to battery power, providing a short transfer time to keep devices running.
Limitations in High-Demand Environments
While line-interactive UPS systems provide adequate protection for many scenarios, they may face limitations in environments with high power demands or frequent power fluctuations. Let's explore some potential challenges:
1. Battery Capacity and Runtime
High-demand scenarios often require UPS systems with larger battery capacities to sustain critical equipment during extended outages. Line-interactive UPS models typically have limited battery runtime compared to their online counterparts. If power outages are frequent or prolonged, the batteries may deplete quickly, leading to potential downtime.
2. Inverter Overload
During power fluctuations or outages, the UPS inverter is responsible for converting battery power to AC power for connected devices. In high-demand environments, the inverter may become overloaded if the combined power consumption of the equipment exceeds its capacity. This can result in system instability, potential equipment damage, and even UPS failure.
3. Voltage Regulation Capabilities
Line-interactive UPS systems utilize an autotransformer to regulate voltage fluctuations within a certain range. However, in areas with severe voltage instability or frequent brownouts, the autotransformer may not be sufficient to maintain a stable output voltage. This can lead to equipment malfunction or damage.
4. Switching Time
While line-interactive UPS systems offer relatively fast switchover times to battery power, there is still a brief interruption in power during the transition. For highly sensitive equipment that requires seamless power continuity, even a momentary interruption can disrupt operations or cause data loss.
Considerations for High-Demand Scenarios
When selecting a UPS system for high-demand environments, it's crucial to carefully assess the power requirements, the frequency and duration of power disturbances, and the sensitivity of the connected equipment. Consider the following recommendations:
Evaluate Power Needs: Accurately determine the total power consumption of the equipment to be protected and choose a UPS system with sufficient capacity.
Battery Capacity: Opt for a UPS with extended battery runtime to ensure adequate backup power during prolonged outages.
Inverter Capacity: Select a UPS with a robust inverter that can handle the peak power demands of the connected equipment.
Voltage Regulation: Consider UPS models with advanced voltage regulation capabilities to mitigate the impact of severe voltage fluctuations.
Online UPS Option: For highly critical applications that require seamless power continuity, explore online UPS systems that provide continuous double-conversion power protection.
Line-interactive UPS systems offer a reliable power protection solution for various applications. However, in high-demand scenarios with frequent power fluctuations or extended outages, their limitations regarding battery capacity, inverter overload, voltage regulation, and switching time should be carefully considered. By understanding these limitations and choosing the appropriate UPS system based on specific power requirements, businesses can ensure optimal protection for their critical equipment and minimize the risk of downtime and data loss.