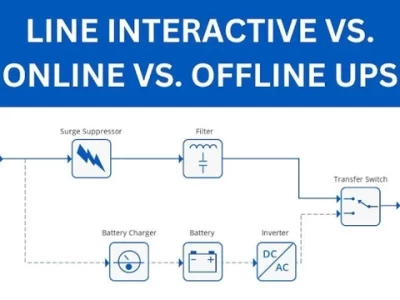
Line-Interactive UPS: Avoid Overspending vs Under-Protecting
Line-Interactive UPS Systems: A Balancing Act
Line-interactive uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) occupy a middle ground between the basic standby UPS and the more complex online double-conversion UPS systems. They offer a blend of affordability and power protection suitable for various applications. However, choosing the right line-interactive UPS requires careful consideration of power needs and system capabilities. Oversizing leads to unnecessary expenses, while under-sizing leaves equipment vulnerable to power disruptions. This article outlines the key steps to accurately size a line-interactive UPS and achieve optimal power protection.
Visit Our UPS Systems Study Course
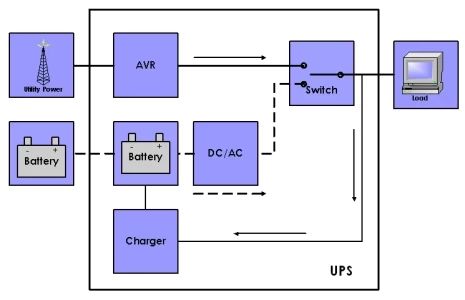
Understanding Line-Interactive UPS Functionality
Line-interactive UPS systems constantly monitor incoming power and regulate voltage fluctuations through an automatic voltage regulator (AVR). This feature is crucial in regions prone to brownouts or voltage sags. Unlike standby UPS systems, line-interactive models switch to battery power only when the input voltage falls significantly or completely fails. This design offers improved protection compared to standby systems while maintaining efficiency.
Step 1: Identifying Your Protected Load
Begin by creating a comprehensive list of all devices you intend the UPS to power in the event of an outage. Note down the following for each device:
Device Type: Computer, server, networking gear, monitor, etc.
Power Rating: This is usually found on a label or in the device's technical specifications. Look for the power consumption in watts (W) or volt-amperes (VA).
Step 2: Calculating Total Power Requirements
Watts vs. Volt-Amperes: If the equipment power ratings are in VA, you may need to convert them to watts. Many devices, especially computer power supplies, have a power factor (PF) of less than 1. A typical estimate is a PF of 0.8. To convert from VA to watts, use the formula: Watts = VA x PF.
Add Up the Load: Once you have all power ratings in watts, total them to arrive at your connected load.
Step 3: Factoring in Growth and Runtime Needs
Future Expansion: Leave approximately 20% headroom in your calculated load to accommodate adding devices in the future.
Desired Runtime: Determine how long you want the UPS to power your equipment during an outage. Remember, the larger the battery capacity of the UPS, the longer the runtime, but also the higher the cost. Refer to vendor-provided runtime charts for estimates based on your connected load.
Step 4: Selecting the Right UPS Capacity
Now that you have your estimated total load (with headroom) and your desired runtime, you can start looking at specific line-interactive UPS models. Choose a UPS where:
- The UPS's load capacity (in watts or VA) exceeds your calculated total needs.
- The UPS's runtime at your estimated load matches or exceeds your desired runtime.
Additional Considerations
Special Power Requirements: If specific devices have sensitive power requirements or high inrush currents (like laser printers), factor this into your load calculation or choose a UPS model with special accommodating features.
Expandable Battery Options: Some line-interactive UPS units support adding external battery packs to boost runtime significantly. Consider this option if you need long backup times.
Energy Efficiency: Line-interactive UPS models may differ in efficiency. Selecting a more efficient model saves energy costs over time, especially in normal operating mode.
Example
Let's imagine you need to protect a desktop computer (250W), monitor (50W), router (20W), and an external hard drive (15W). Your total initial load is 335W. With a 20% growth margin, you'd target around 400W. If you want a 15-minute runtime at that load, you'd look for a line-interactive UPS with a capacity of at least 400W and a stated runtime exceeding 15 minutes under similar load conditions.
By meticulously calculating your power needs and considering future growth, you can select the right-sized line-interactive UPS. This ensures reliable protection for your essential equipment, maximizes runtime, and optimizes your investment in power backup infrastructure.
Making the Right Choice
Selecting the appropriate line-interactive UPS requires a comprehensive understanding of power needs, system capabilities, and desired features. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure optimal protection for your critical equipment without unnecessary overspending. Remember to consider future expansion plans and potential changes in power requirements to choose a UPS system that will serve your needs effectively for years to come.