Battery Advancements and the Impact on Line-Interactive UPS
Advancements in Battery Technology and Their Impact on Line-Interactive UPS
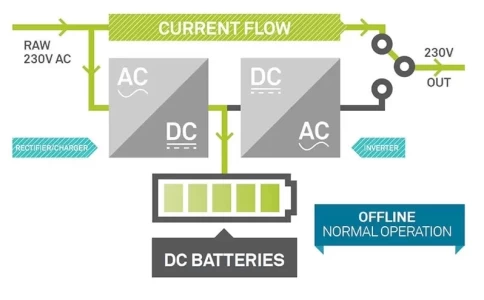
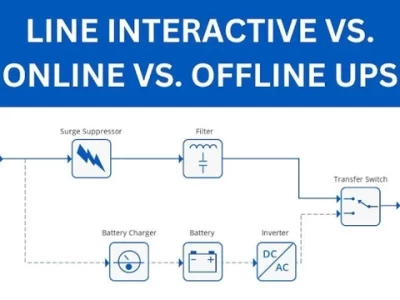
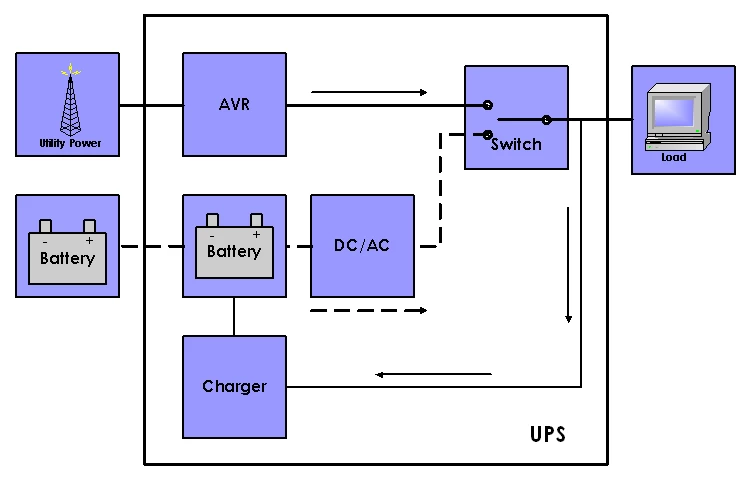
Line-interactive uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems play a crucial role in ensuring power continuity for sensitive electronic equipment. Serving as a safeguard against power disruptions, these systems seamlessly switch to battery backup during outages, preventing data loss, equipment damage, and downtime. Recent advancements in battery technology, particularly lithium-ion batteries, have significantly influenced the capabilities and performance of line-interactive UPS systems.
Visit Our UPS Systems Study Course
Lithium-ion: The Emerging Choice
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, widely known for their use in laptops and electric vehicles, are increasingly finding their way into UPS systems. Here's how they stand out:
Higher Energy Density: Li-ion batteries pack more energy into a smaller and lighter form factor compared to lead-acid counterparts. This translates to space-saving UPS units or more runtime within the same footprint.
Longer Lifespan: Li-ion batteries boast more charge/discharge cycles than lead-acid batteries. This could mean less frequent battery replacements over the lifetime of the UPS system, reducing maintenance costs.
Faster Recharge Times: Li-ion batteries generally recharge faster, contributing to quicker recovery times between outages.
Efficient Operation: Reduced internal resistance leads to greater efficiency in charging and discharging, thus minimizing energy losses.
Considerations and Trade-offs
Cost: Currently, Li-ion-based UPS systems typically carry a higher initial price tag compared to those using lead-acid batteries. However, the total cost of ownership over time may be comparable or even favorable due to their longevity and lower maintenance.
Management Complexity: Li-ion batteries sometimes require more sophisticated battery management systems (BMS) for safe and optimal operation.
Safety: Certain Li-ion chemistries, if mishandled, have greater potential for thermal runaway than traditional lead-acid batteries. Reputable manufacturers prioritize robust design and safety measures in their Li-ion UPS units.
Other Battery Advancements
Enhanced Lead-Acid Batteries: Developments like Thin Plate Pure Lead (TPPL) and Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) technologies have improved lead-acid battery performance in areas like cycle life, recharge times, and tolerance to temperature fluctuations.
Alternative Chemistries: Flow batteries, sodium-ion batteries, and more offer unique characteristics potentially relevant to specific UPS use cases.
The Impact on Line-Interactive UPS
The integration of advanced battery technologies into line-interactive UPS designs brings about notable implications:
Compact Designs: Smaller batteries open up possibilities for more streamlined and space-efficient line-interactive units, particularly valuable in edge computing and cramped network closets.
Increased Reliability: Longer battery lifespan and resilience towards environmental conditions enhance UPS system reliability overall.
Extended Runtimes: Depending on the application, advanced batteries may unlock longer backup times on smaller line-interactive units.
Eco-Friendliness: Li-ion batteries have the potential for greater recyclability than lead-acid options, minimizing environmental impact at end-of-life.
Choosing the Right Battery Technology
The optimal battery choice for your line-interactive UPS depends on several factors:
Criticality of the Load: For highly critical applications, the added longevity and performance of Li-ion batteries often justify the cost.
Space Constraints: Where installation space is extremely limited, the compactness of Li-ion solutions becomes a major advantage.
Environmental Conditions: If the UPS is in a less temperature-controlled environment, the robustness of newer lead-acid technologies or some advanced options might be preferable.
Budget: If the initial purchase cost is the primary driver, a traditional lead-acid line-interactive UPS may still be the most practical solution.
The advancements in battery technology are transforming the landscape of line-interactive UPS systems, enhancing their efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. As lithium-ion batteries continue to evolve and decrease in cost, they are expected to become the standard choice for new UPS installations, offering significant advantages over traditional battery technologies. Organizations looking to upgrade or install new UPS systems should consider the long-term benefits of lithium-ion batteries, despite the initial higher investment, to ensure reliable and efficient power backup solutions.