Cybersecurity for Protective Devices
Motor Protection
Improving Energy Efficiency Through Motor Protection
Transformer Protection
Conventional Methods to AI-Based Solutions
Lightning Protection Systems
Advancements in Lightning Rod Design: Early Streamer Emission (ESE) Technology
Overcurrent and Short Circuit Protection
Coordinating Overcurrent Protection in Complex Power Systems
Generator Protection
The Evolution of Generator Fault Detection
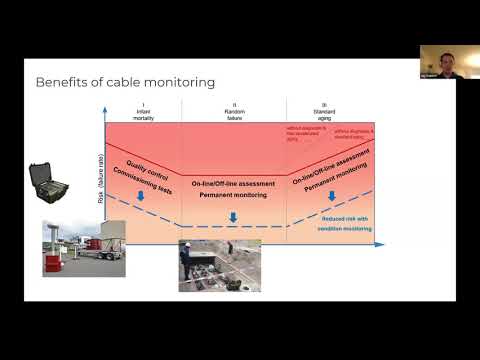
Electrical Protection
Securing Communication and Data Integrity
The ever-growing complexity of electrical grids, with their increasing reliance on interconnected communication and data exchange, necessitates robust cybersecurity measures. Traditional security solutions struggle to keep pace with the evolving sophistication of cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure. Blockchain technology, with its core principles of immutability, transparency, and distributed ledger technology, offers a promising approach for enhancing communication security and data integrity within electrical grids. This article explores the application of blockchain in electrical grids, focusing on its role in ensuring data integrity and enhancing secure communication.
Visit Our Electrical Protection Study Course
Blockchain Fundamentals in Electrical Grids
Blockchain technology, at its core, is a distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. In the context of electrical grids, it offers a decentralized framework for managing data exchanges, where each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one, ensuring a secure and traceable record.
The Imperative for Enhanced Communication and Data Security
Modern electrical grids rely on real-time communication and data exchange between various components, including protective relays, smart meters, and control centers. These interconnected systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks that can disrupt operations, manipulate data, or compromise system integrity. Traditional security solutions, such as firewalls and encryption,...